Alberta
Province pumps healthcare system – $100M boost for surgical suites, equipment, rural hospitals

From the Province of Alberta
A $100-million government investment will help hospitals across the province upgrade their operating rooms to provide thousands more surgeries to Albertans.
Large-scale renovations and some new operating rooms in Edmonton, Calgary, Grande Prairie and Lethbridge will allow those hospitals to focus on providing more complex surgeries, leaving rural sites and chartered surgical facilities to provide additional lower risk surgeries.
“Albertans deserve a world-class health system that delivers the right care, in the right setting, at the right time. This funding from Budget 2020 will drive down wait times with necessary and overdue upgrades to hospital operating rooms and equipment across the province. Ultimately, we will make sure our health-care system has the capacity and the staff to deliver the best access to surgery in Canada.”
“This is great news for Albertans who need surgeries and want more access to quality health care in their home communities. This $100 million for capital projects will have a cascading effect, improving access to surgeries in big city hospitals, but also in rural communities across the province, so people can get care closer to home. It’s just the start of our government’s commitment to ensure the success of the Alberta Surgical Initiative. We are working exceptionally hard to ensure we build the best health system possible in this wonderful province.”
This capital funding is part of the government’s $500-million commitment in Budget 2020 to drive down wait times and provide all medically necessary surgeries within clinically appropriate times. Savings found through the AHS Reviewwill support this initiative.
The $100 million in capital funding will be spent on surgical infrastructure and equipment, including:
- Upgrades to 12 operating rooms at Calgary’s Foothills Medical Centre. Low-risk surgeries will be moved out of the Foothills hospital and offered in Canmore, High River and independent surgical facilities in Calgary, relieving pressures on city hospitals with long wait lists.
- A fit-out of an operating room in Grande Prairie and converting space in the Edson Health Centre into a second operating room.
- Renovations at the Rocky Mountain House Health Centre so it can perform more endoscopy procedures and create more space in the Red Deer hospital to focus on more complex surgeries. Low-risk surgeries will also be moved out of the Red Deer Hospital to be offered in Innisfail, Stettler, Ponoka and Olds.
- Renovations to operating departments at the Royal Alexandra Hospital and the University of Alberta Hospital, including the addition of one new operating room. Lower risk procedures will be moved to the Fort Saskatchewan Health Centre, the Grey Nuns Community Hospital and the Sturgeon Community Hospital in St. Albert.
- Renovations at the Medicine Hat Regional Hospital.
- Combining two smaller operating rooms into one larger space for more complex surgeries at Lethbridge’s Chinook Regional Hospital.
This capital investment will help AHS add over 17,000 surgeries this fiscal year to meet the four-year target that was set. Once the renovations are complete and less complex surgeries are being performed in chartered surgical facilities, up to 30,000 additional surgeries will be available to Albertans by 2023.
Alberta
Alberta Precipitation Update

Below are my updated charts through April 2025 along with the cumulative data starting in October 2024. As you can see, central and southern Alberta are trending quite dry, while the north appears to be faring much better. However, even there, the devil is in the details. For instance, in Grande Prairie the overall precipitation level appears to be “normal”, yet in April it was bone dry and talking with someone who was recently there, they described it as a dust bowl. In short, some rainfall would be helpful. These next 3 months are fairly critical.
Thanks for reading William’s Substack!
Subscribe for free to receive new posts and support my work.
Alberta
Alberta’s move to ‘activity-based funding’ will improve health care despite naysayer claims

From the Fraser Institute
After the Smith government recently announced its shift to a new approach for funding hospitals, known as “activity-based funding” (ABF), defenders of the status quo in Alberta were quick to argue ABF will not improve health care in the province. Their claims are simply incorrect. In reality, based on the experiences of other better-performing universal health-care systems, ABF will help reduce wait times for Alberta patients and provide better value-for-money for taxpayers.
First, it’s important to understand Alberta is not breaking new ground with this approach. Other developed countries shifted to the ABF model starting in the early 1990s.
Indeed, after years of paying their hospitals a lump-sum annual budget for surgical care (like Alberta currently), other countries with universal health care recognized this form of payment encouraged hospitals to deliver fewer services by turning each patient into a cost to be minimized. The shift to ABF, which compensates hospitals for the actual services they provide, flips the script—hospitals in these countries now see patients as a source of revenue.
In fact, in many universal health-care countries, these reforms began so long ago that some are now on their second or even third generation of ABF, incorporating further innovations to encourage an even greater focus on quality.
For example, in Sweden in the early 1990s, counties that embraced ABF enjoyed a potential cost savings of 13 per cent over non-reforming counties that stuck with budgets. In Stockholm, one study measured an 11 per cent increase in hospital activity overall alongside a 1 per cent decrease in costs following the introduction of ABF. Moreover, according to the study, ABF did not reduce access for older patients or patients with more complex conditions. In England, the shift to ABF in the early to mid-2000s helped increase hospital activity and reduce the cost of care per patient, also without negatively affecting quality of care.
Multi-national studies on the shift to ABF have repeatedly shown increases in the volume of care provided, reduced costs per admission, and (perhaps most importantly for Albertans) shorter wait times. Studies have also shown ABF may lead to improved quality and access to advanced medical technology for patients.
Clearly, the naysayers who claim that ABF is some sort of new or untested reform, or that Albertans are heading down an unknown path with unmanageable and unexpected risks, are at the very least uninformed.
And what of those theoretical drawbacks?
Some critics claim that ABF may encourage faster discharges of patients to reduce costs. But they fail to note this theoretical drawback also exists under the current system where discharging higher-cost patients earlier can reduce the drain on hospital budgets. And crucially, other countries have implemented policies to prevent these types of theoretical drawbacks under ABF, which can inform Alberta’s approach from the start.
Critics also argue that competition between private clinics, or even between clinics and hospitals, is somehow a bad thing. But all of the developed world’s top performing universal health-care systems, with the best outcomes and shortest wait times, include a blend of both public and private care. No one has done it with the naysayers’ fixation on government provision.
And finally, some critics claim that, under ABF, private clinics will simply focus on less-complex procedures for less-complex patients to achieve greater profit, leaving public hospitals to perform more complex and thus costly surgeries. But in fact, private clinics alleviate pressure on the public system, allowing hospitals to dedicate their sophisticated resources to complex cases. To be sure, the government must ensure that complex procedures—no matter where they are performed—must always receive appropriate levels of funding and similarly that less-complex procedures are also appropriately funded. But again, the vast and lengthy experience with ABF in other universal health-care countries can help inform Alberta’s approach, which could then serve as an example for other provinces.
Alberta’s health-care system simply does not deliver for patients, with its painfully long wait times and poor access to physicians and services—despite its massive price tag. With its planned shift to activity-based funding, the province has embarked on a path to better health care, despite any false claims from the naysayers. Now it’s crucial for the Smith government to learn from the experiences of others and get this critical reform right.
-

 Autism2 days ago
Autism2 days agoNIH, CMS partner on autism research
-

 Economy1 day ago
Economy1 day agoCanada’s Energy Wealth Is Bleeding South
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoInnovative Solutions Like This Plan To Provide Power For Data Centres Will Drive Natural Gas Demand For Decades
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta’s move to ‘activity-based funding’ will improve health care despite naysayer claims
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTrump announces UK will fast-track American products under new deal
-

 espionage1 day ago
espionage1 day agoHong Kong Police Detain Relatives of Canadian Candidate Targeted by Beijing Election Interference
-

 Crime10 hours ago
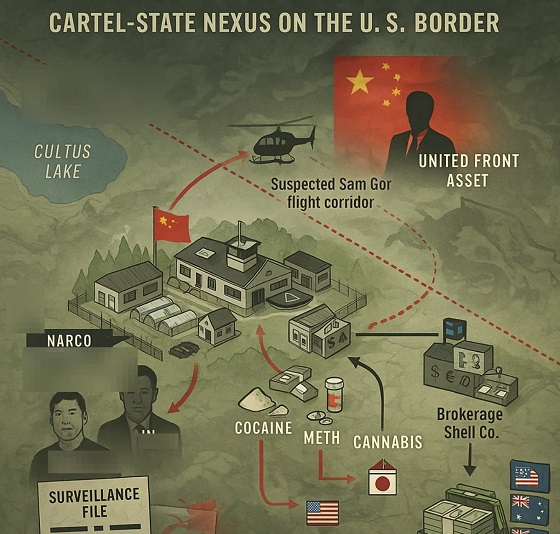
Crime10 hours agoHow the CCP’s United Front Turned Canada’s Legal Cannabis Market into a Global Narcotics Brokerage Network
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoCardinals elect Robert Francis Prevost, first American pope to lead Catholic church